What is CDN?
A content delivery network (CDN) is a network of interconnected servers that speeds up webpage loading for data-heavy applications.
CDN stand for content delivery network or content distribution network. When a user visits a website, data from that website's server has to travel across the internet to reach the user's computer.
If the user is located far from that server, it will take a long time to load a large file, such as a video or website image.
Instead, the website content is stored on CDN servers geographically closer to the users and reaches their computers much faster.
Why CDN is important?
Content delivery networks (CDNs) provide many benefits that improve website performance and support core network infrastructure. For example, a CDN can do the following tasks:
Reduce page load time.
Reduce bandwidth Costs.
Increase content availability.
Improve website security.
How does a CDN work?
Content delivery networks (CDNs) work by establishing a point of presence (POP) or a group of CDN edge servers at multiple geographical locations.
This geographically distributed network works on the principles of caching, dynamic acceleration, and edge logic computations.
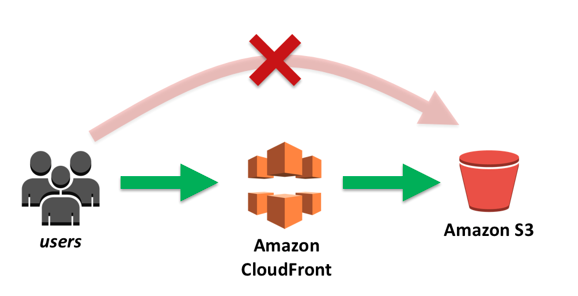
What is Amazon CloudFront?
Amazon CloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN) service built for high performance, security, and developer convenience. You can use Amazon CloudFront to do these tasks:
Deliver data through 450+ globally dispersed points of presence (POPs) with automated network mapping and intelligent routing.
Improve security with traffic encryption and access controls, and use AWS Shield Standard to defend against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks at no additional charge.
Customize the code you run at the AWS network edge using serverless compute features to balance cost, performance, and security.
Scale automatically to deliver software, game patches, and IoT updates with high transfer rates.